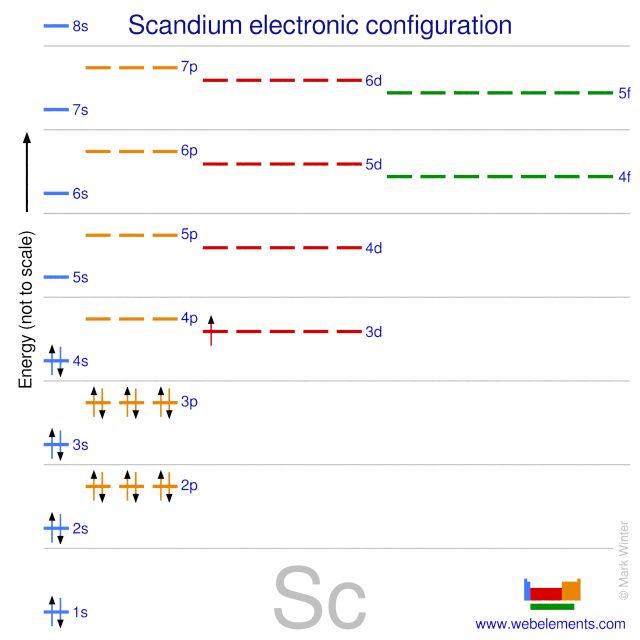
- Sc Name of Element: Scandium Atomic Weight: 45.0 Atomic Number: 21. Atomic Weight: 227.0 Atomic Number: 89 Group: Transition Metals Electron Configuration.
- Scandium iodide (ScI3) is used in lamps that produce light having a color closely matching natural sunlight. Atomic Number 21 Learn more about the atomic number. Description Fairly soft, silvery-white metal. Eighth most abundant 'rare earth' found in the earth's crust (5.0 ppm). Atomic Mass 44,95591 Learn more about the atomic mass.
- Scandium is the 31 st most abundant element on Earth, according to Periodic Table, with about 22 parts per million abundance by weight in Earth's crust, according to Chemicool.
Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic d-block element, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids. It was discovered in 1879 by spectral analysis of the minerals euxenite and gadolinite from Scandinavia. ››More information on molar mass and molecular weight. In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all of these products together.
Molar mass of Sc = 44.955910 g/mol
Convert grams Scandium to moles or moles Scandium to grams
| Symbol | # of Atoms | Scandium | Sc | 44.955910 | 1 | 100.000% |
Note that all formulas are case-sensitive.Did you mean to find the molecular weight of one of these similar formulas?
SC
Sc


In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all of these products together.
If the formula used in calculating molar mass is the molecular formula, the formula weight computed is the molecular weight. The percentage by weight of any atom or group of atoms in a compound can be computed by dividing the total weight of the atom (or group of atoms) in the formula by the formula weight and multiplying by 100.

The atomic weights used on this site come from NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology. We use the most common isotopes. This is how to calculate molar mass (average molecular weight), which is based on isotropically weighted averages. This is not the same as molecular mass, which is the mass of a single molecule of well-defined isotopes. For bulk stoichiometric calculations, we are usually determining molar mass, which may also be called standard atomic weight or average atomic mass.
Using the chemical formula of the compound and the periodic table of elements, we can add up the atomic weights and calculate molecular weight of the substance.
Formula weights are especially useful in determining the relative weights of reagents and products in a chemical reaction. These relative weights computed from the chemical equation are sometimes called equation weights.
Atomic Number List
Finding molar mass starts with units of grams per mole (g/mol). When calculating molecular weight of a chemical compound, it tells us how many grams are in one mole of that substance. The formula weight is simply the weight in atomic mass units of all the atoms in a given formula.
A common request on this site is to convert grams to moles. To complete this calculation, you have to know what substance you are trying to convert. The reason is that the molar mass of the substance affects the conversion. This site explains how to find molar mass.
Scandium Atomic Mass Number
Chemical properties of scandium - Health effects of scandium - Environmental effects of scandium
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Scandium Scandium is a soft, silvery transition element which occurs in rare minerals from Scandinavia. It develops a slightly yellowish or pinkish cast when exposed to air. Scandium tarnished in air and burn easily, once it has been ignited. It reacts with water to form hydrogen gas and will dissolve in many acids. Pure scandium is produced by heating scandium fluoride (ScF3) with calcium metal. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Scandium has no biological role. Only trace amounts reach the food chain, so the average person's daily intake is less than 0.1 microgram. Scadium is not toxic, although there have been suggestions that some of its compounds might be cancerogenic. Scandium is mostly dangerous in the working environment, due to the fact that damps and gasses can be inhaled with air. This can cause lung embolisms, especially during long-term exposure. Scandium can be a threat to the liver when it accumulates in the human body. |
Effects of scandium on the environment
Scandium is dumped in the environment in many different places, mainly by petrol-producing industries. It can also enter the environment when household equipment is thrown away. Scandium will gradually accumulate in soils and water soils and this will eventually lead to increasing concentrations in humans, animals and soil particles. |
Back to the periodic table of elements
More from 'Elements'
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Atomic Mass
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Mass Number
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Scandium Neutrons
Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved
